8. AIRFOIL
Aerofoil Shape and Its Function
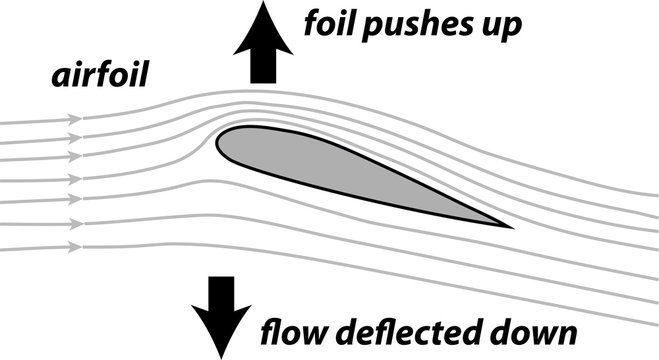
An aerofoil (or airfoil) is a specially designed shape that is used in various applications, primarily in aircraft wings, to generate lift and reduce drag. Here’s how it works:
Design
- Shape: An aerofoil typically has a curved upper surface and a flatter lower surface. This asymmetrical shape is crucial for its operation.
- Angle of Attack: The angle at which the aerofoil meets the oncoming air is known as the angle of attack. Adjusting this angle can significantly impact lift generation.
How It Works
- Airflow: As the aircraft moves forward, air flows over and under the aerofoil.
- Pressure Difference: The design of the aerofoil causes the air pressure on top of the aerofoil to be lower than the pressure underneath it. This happens due to the faster airflow over the curved top surface, which reduces the pressure, according to Bernoulli’s principle.
- Lift Generation: The difference in pressure creates an upward force called lift, allowing the aircraft to rise into the air.
- Drag: While generating lift, the aerofoil also experiences drag, which is the resistance of the air against the motion. Designers aim to minimize this drag to improve efficiency.
Applications
Aerofoils are not limited to aircraft wings; they can also be found in:
- Propeller blades
- Turbine blades
- Automotive designs (used to enhance performance and stability)
Conclusion
Understanding the aerofoil shape and its mechanics is vital for aerospace engineering, as it plays a crucial role in the performance and efficiency of flight vehicles. Properly designed aerofoils contribute not only to lift generation but also to the overall aerodynamic efficiency of various transportation modalities.